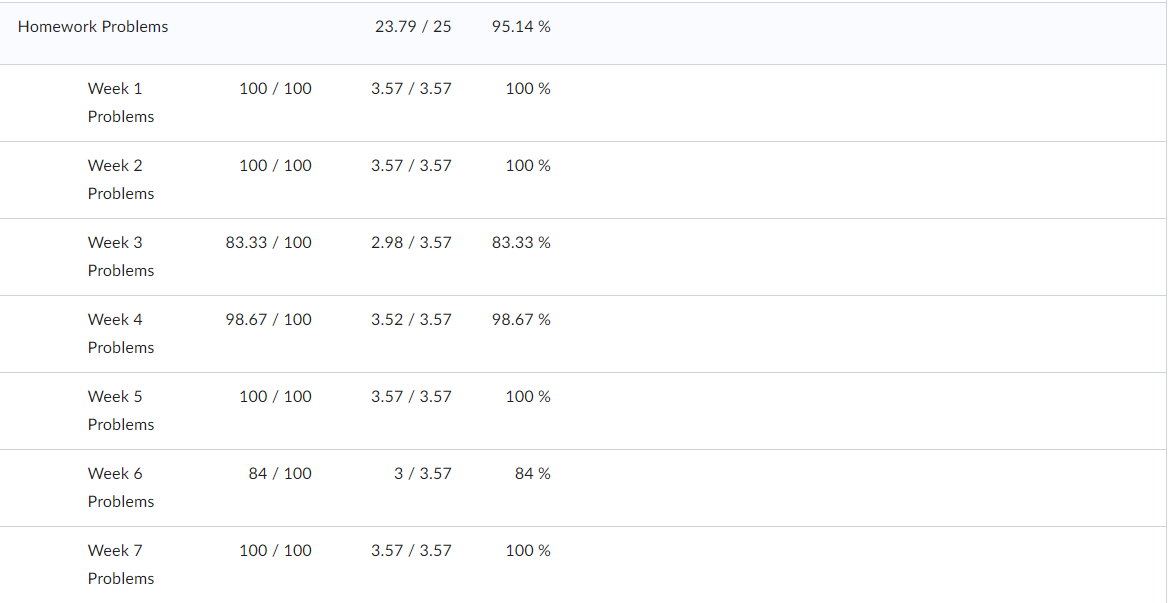
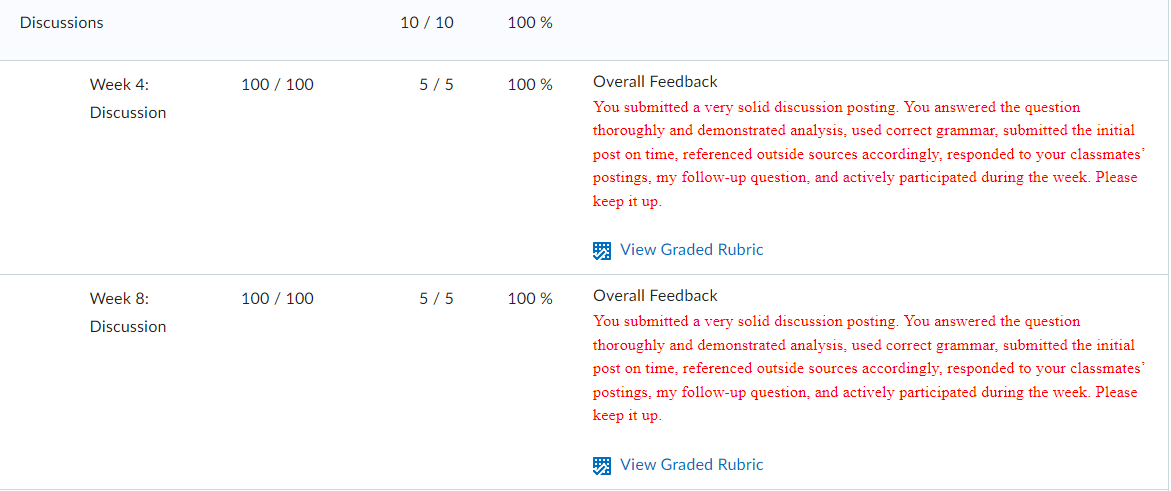
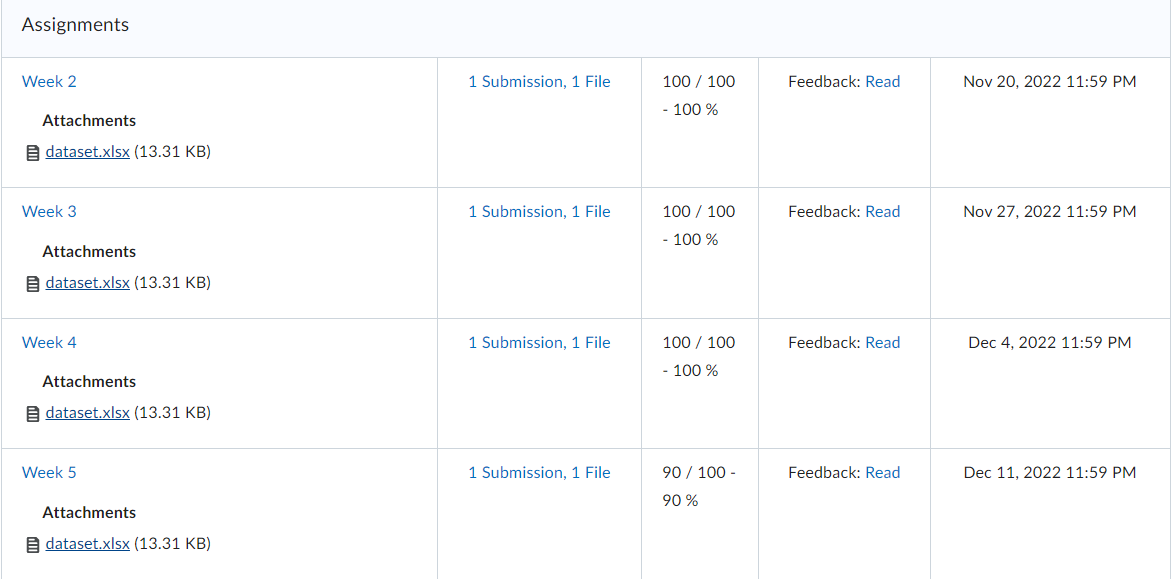
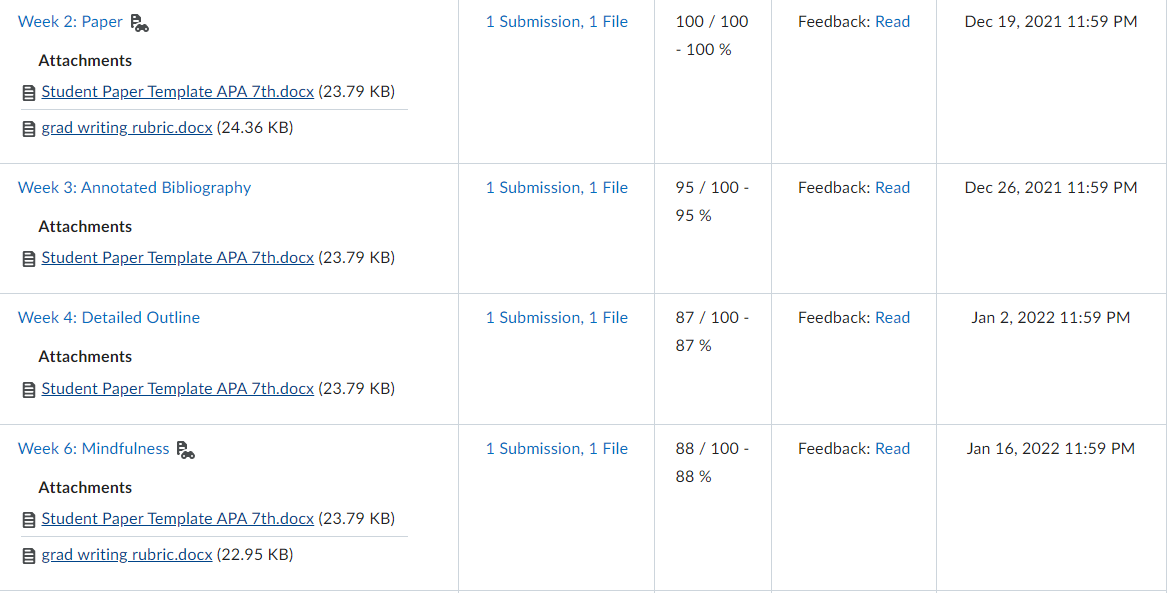
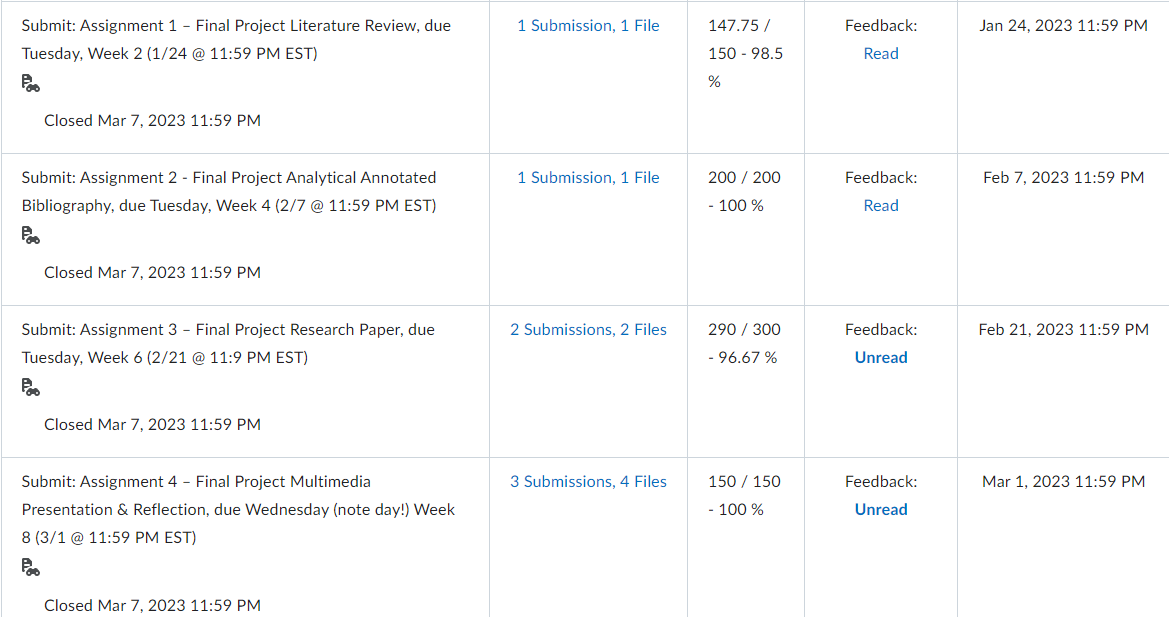
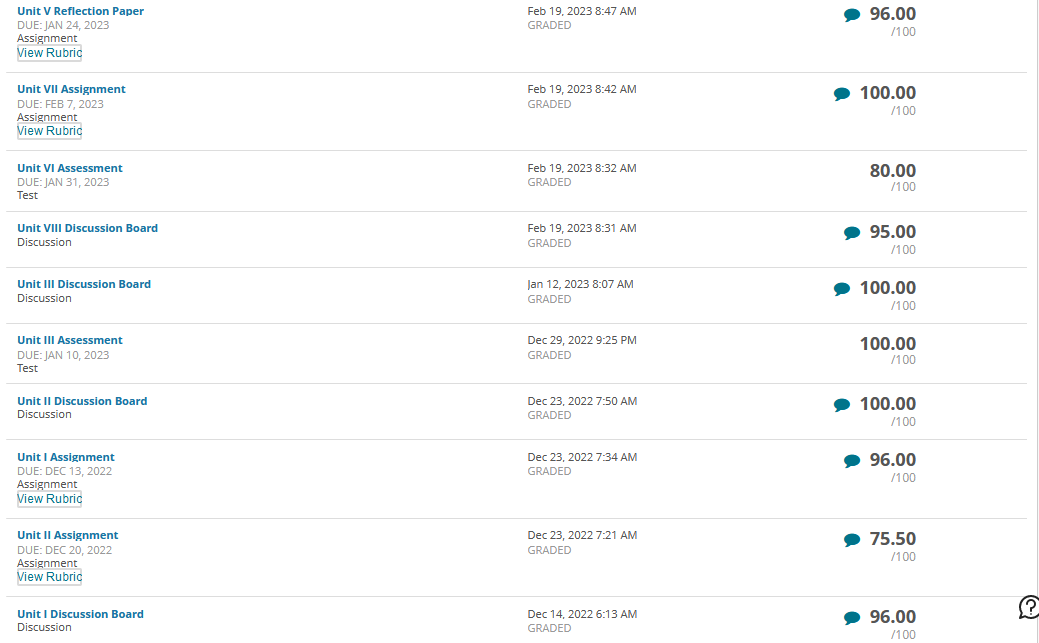
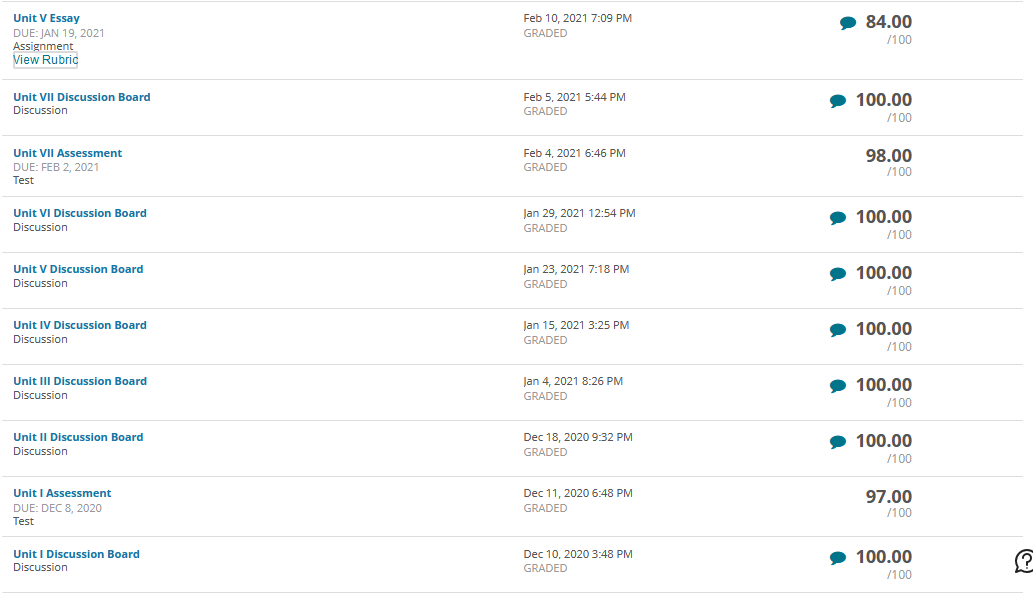
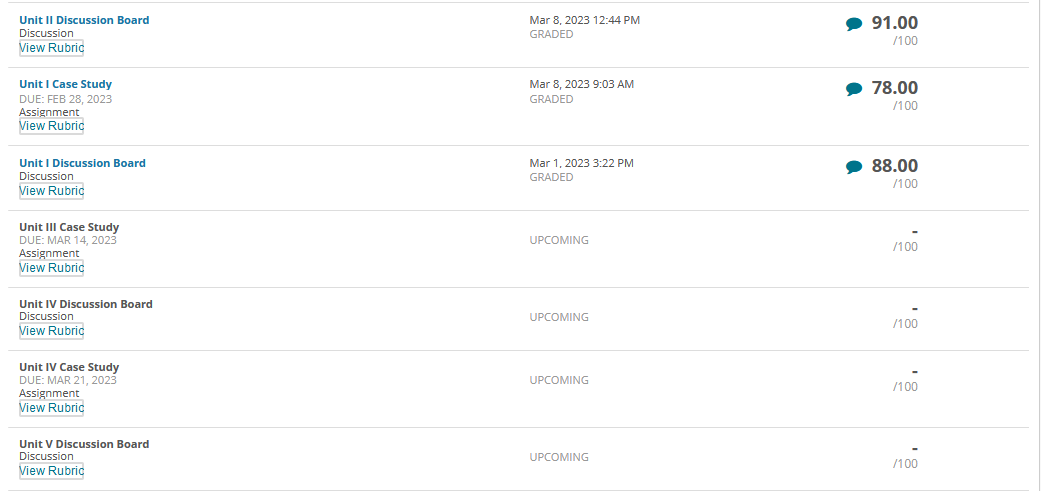
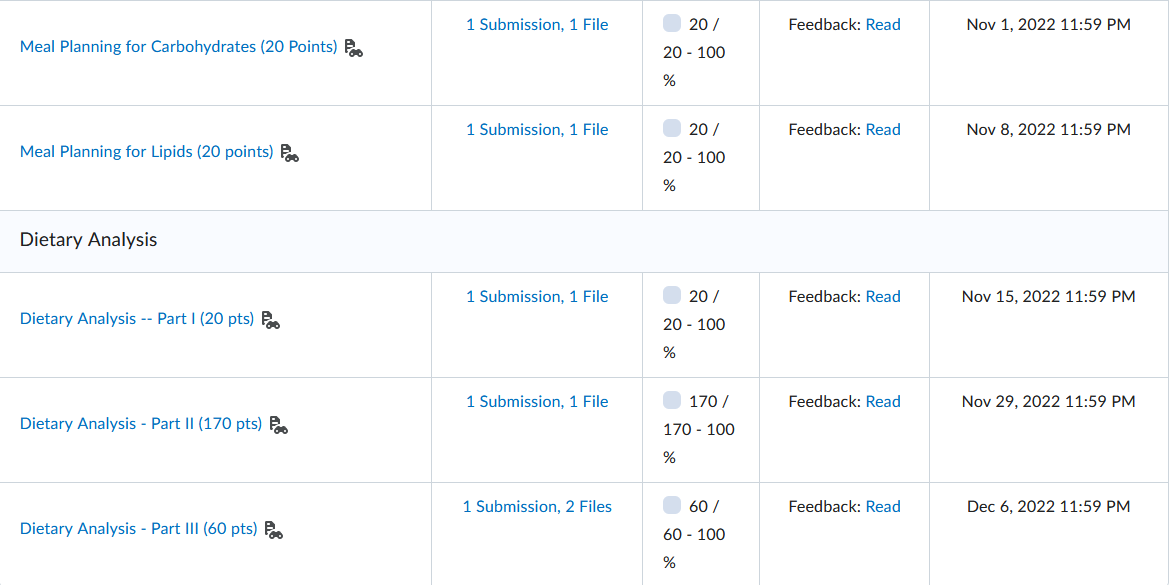
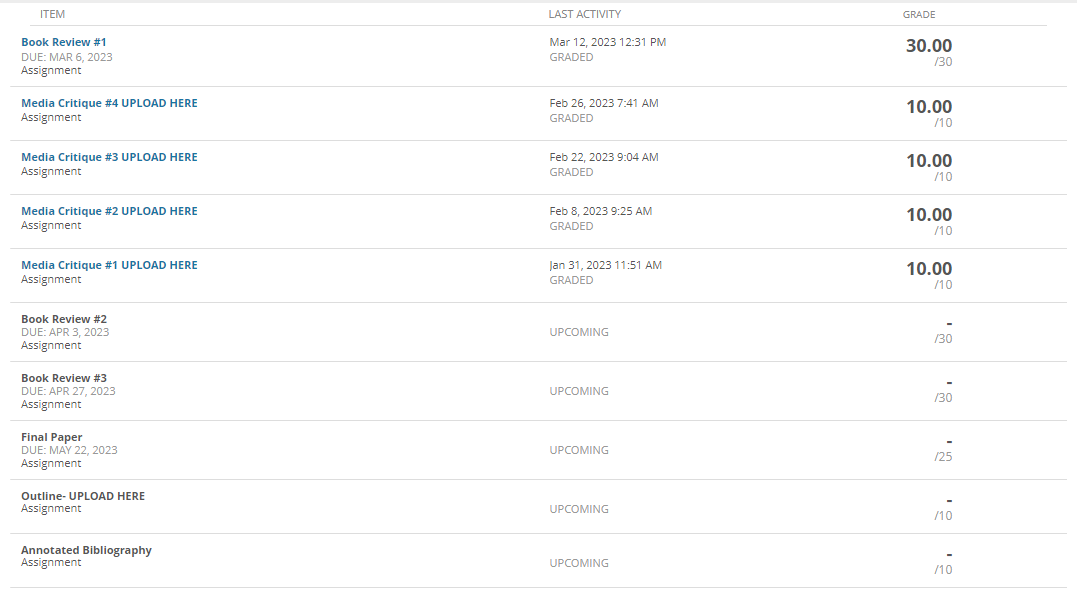
Governance in Japan, Germany, and China has been changing as “western” governance systems have increasingly been adopted. Traditionally, boards of directors in these nations have largely been composed of insider manager directors. In 2015, Japan adopted a new governance code that strongly emphasized the importance of firms to elect many more independent outside directors. Activist shareholders and a strong market for corporate control have traditionally been absent in Japan. More recently, shareholders have been more active and the most successful ones have been labelled “engagement” funds. The change is signaled, for example, by the Japanese Government Pension Investment Fund choosing an activist investor, the Taiyo Pacific Partners LP—a U.S. based engagement fund —to manage some of its $1 trillion in assets. Furthermore, the Japanese Financial Services Agency has introduced a “stewardship code” that calls on investors to “press for greater returns.” As such, the Japanese environment is becoming more oriented toward “shareholder rights,” although the approach comparatively is not as “activist” as found elsewhere in the world. Besides a new brand of activism in Japan, activism is spreading around the globe including Germany. Again, a revised governance code pushed for more shareholder-friendly governance arrangements, including an emphasis on outside directors and stronger emphasis on executive long-term incentive compensation. With stronger emphasis on shareholders’ rights, activist funds pursued more activity. Cevian Capital, an activist fund, is involved in ownership with ThyssenKrupp and Bilfinger. Likewise, Elliott Management, another activist fund, is involved with Celesio and Kabel Deutschland. Although management teams are quite suspicious of activists in Germany and other continental European countries, “Germany is an area where activists may look because of its protections for minority investors in takeover deals.” However, research shows that activist investors have less influence on top management teams because of restrictive governance regulation. For example, one study found that activist investors’ involvement did not lead to increased CEO turnover. Although some activism has taken place in mainland China, firms in Hong Kong have been targeted more by activist funds. Hong Kong-listed companies have been loosening rules for foreign ownership and, therefore, companies have been paying more attention to what investors think in regard to governance and transparency. In mainland China, however, often shares are mostly owned by parent business group firms as well as the government or, because they are often younger, they are still owned by the firm’s founders. As such, there is less potential influence for foreign investors on company decisions. However, the Shanghai-Hong Kong Stock Connect program has accelerated opportunities for activists on the mainland. Through the Connect program, foreign financial institutions can have direct access to mainland China’s capital markets. This means that foreign ownership will have more activist influence because of shareholder voting rights in local mainland China-listed firms. Also, many home-grown Chinese activist funds thrived due to their recent investments in the technology sector with the success of Alibaba, Tencent, and many other high technology firms. But how do owners from emerging market countries and countries with significant government ownership influence the firms they invest in overseas? Interestingly, sovereign wealth funds, many from emerging economies, are playing a dominant role by investing in developed economies as well as other emerging economies. In their own way, they are playing an activist role. For example, since the global financial crisis, many German firms have sought investment from sovereign wealth firms from Gulf States in the Mideast. In particular, many German major automobile firms have recruited Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) sovereign wealth fund investments during the stresses of financial restructuring spurred by the financial crisis.
Thank you so much for this newsletter Thank you so much for this newsletter 7624243 https://t.me appleipnoneipad !
Thank you so much for this newsletter Thank you so much for this newsletter
7624243 https://t.me appleipnoneipad !